The Cybersecurity Express – 17 Jan 2025
The station stood quiet under the pale light of the waning moon, its cobblestones glistening as if polished by an unseen hand. You stand there, clutching your ticket, inscribed with golden letters that read: “Cybersecurity Express.” The air is thick with expectation, a faint whisper carried on the wind as though the very station itself knew the weight of the journey ahead. Above you, a clock ticks steadily, marking the moments until the arrival of the great train that will bear you across the realms of hidden dangers and noble defenses.
At last, it appears, emerging from the shadows like a great silver steed of old, its wheels clanking like the toll of ancient bells. The train halts with a low sigh, and its doors open, inviting you into its glowing, warm interior. The conductor, a figure cloaked in mystery, nods solemnly. “Our first destination,” he says, “a tale of vulnerabilities laid bare and the triumphs of those who guard the gates.” You step aboard, and as the train begins its journey, the landscape of cybersecurity unfolds before you, vast and brimming with stories yet untold.
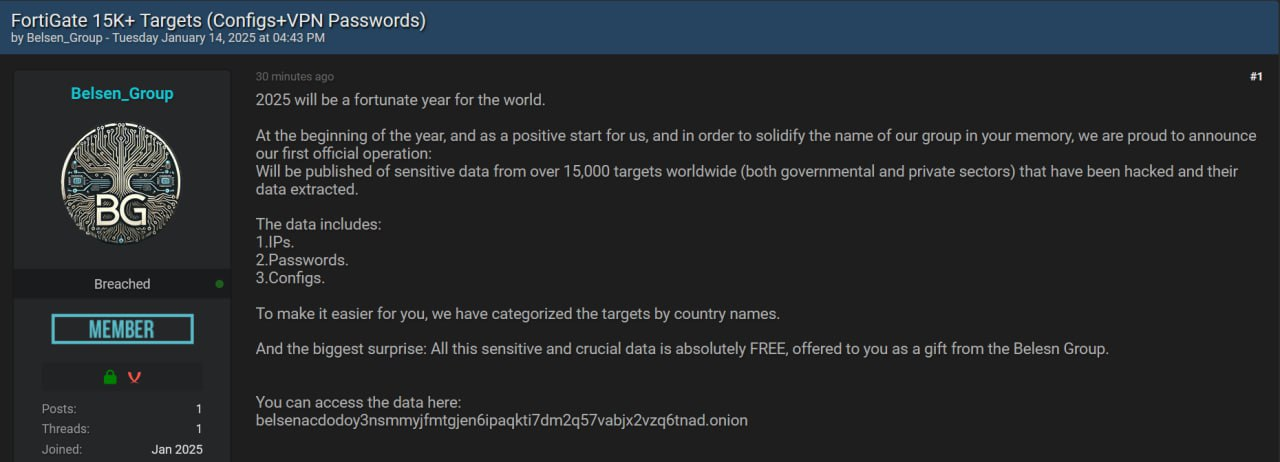
Data From 15,000 Fortinet Firewalls Leaked by Hackers
In a significant cybersecurity breach, a newly formed hacking group known as the Belsen Group has leaked sensitive data from over 15,000 Fortinet FortiGate firewalls. The leak, which surfaced on January 15, 2025, includes configuration files and VPN credentials, posing serious risks to organizations that rely on these devices for network security.
The leaked data comprises a 1.6 GB archive organized by country, with folders containing subdirectories named after individual IP addresses. Each directory holds crucial information, including:
- Configuration files (config.conf)
- Plaintext VPN credentials (vpn-passwords.txt)
- Usernames and passwords
- Private keys and firewall rules
According to cybersecurity experts, the leak appears to be extensive, with the majority of affected devices located in Mexico (1,603), followed by the United States (679) and Germany (208). Many of these devices are deployed in various sectors, including healthcare and government, making the breach particularly alarming.
The Belsen Group claims that the data was obtained through exploiting vulnerabilities in Fortinet devices. Specifically, the group is believed to have leveraged a zero-day vulnerability tracked as CVE-2022-40684, which was actively exploited before a patch was released. This vulnerability allowed attackers to download configuration files from targeted FortiGate devices and create unauthorized super_admin accounts.
The attack vector likely involved unauthorized administrative logins on management interfaces of the firewalls. Once inside, attackers could alter configurations and extract sensitive credentials using techniques such as DCSync, which simulates a domain controller to extract password hashes for Active Directory accounts.
The implications of this data leak are profound. With access to configuration files and credentials, malicious actors can potentially infiltrate networks, modify firewall settings, and execute further attacks within compromised environments. The availability of plaintext VPN credentials significantly increases the risk of unauthorized remote access to sensitive systems.
Security experts urge organizations that utilize Fortinet devices to take immediate action:
- Assess Exposure: Organizations should check if their devices are among those listed in the leaked data and verify their patch history for CVE-2022-40684.
- Change Credentials: It is critical to change all admin and VPN credentials associated with affected devices immediately.
- Review Firewall Rules: Organizations should conduct thorough reviews of their firewall rules to identify any unauthorized changes or vulnerabilities.
- Implement Enhanced Monitoring: Deploy intrusion detection systems (IDS) and security information and event management (SIEM) solutions to monitor for unusual activity indicative of exploitation attempts.
- Regular Security Audits: Conduct routine security assessments to identify potential vulnerabilities in network infrastructure.
The leak of sensitive data from over 15,000 Fortinet firewalls by the Belsen Group underscores the growing threat posed by cybercriminals targeting critical infrastructure. As organizations scramble to secure their systems in light of this breach, it is essential for them to adopt robust cybersecurity measures and remain vigilant against evolving threats. The incident serves as a stark reminder of the vulnerabilities inherent in interconnected systems and highlights the need for continuous improvement in cybersecurity practices across all sectors.
Over 660,000 Rsync servers exposed to code execution attacks
In a concerning development for cybersecurity, over 660,000 Rsync servers have been exposed to critical vulnerabilities that could allow attackers to execute arbitrary code remotely. This alarming statistic comes from recent findings by security researchers, who identified six significant vulnerabilities in the widely used file synchronization tool, Rsync. These flaws pose serious risks to organizations that rely on Rsync for data transfers and backups.
The vulnerabilities were disclosed following research by teams from Google Cloud and independent security experts. Among the most critical is CVE-2024-12084, a heap-based buffer overflow with a CVSS score of 9.8, indicating its severity. This flaw arises from improper handling of checksum lengths in the Rsync daemon, allowing an attacker with anonymous read access to execute arbitrary code on the server running Rsync. Other notable vulnerabilities include:
- CVE-2024-12085: An information leak vulnerability that allows attackers to extract uninitialized stack data during file checksum comparisons.
- CVE-2024-12086: A server-side flaw enabling arbitrary file enumeration from connected client systems during file synchronization.
- CVE-2024-12087: A path traversal vulnerability that permits malicious servers to write files outside intended directories.
- CVE-2024-12088: A bypass of the –safe-links option, which can lead to unauthorized file writes.
- CVE-2024-12747: A race condition in symbolic link processing that could allow privilege escalation or sensitive information disclosure.
These vulnerabilities primarily affect Rsync versions prior to 3.4.0, which was released on January 14, 2025, to address these critical security issues.
The widespread exposure of Rsync servers is particularly alarming given their extensive use in various sectors, including backup systems, public file distribution, and cloud management operations. A Shodan search revealed that many of these servers are publicly accessible, with a significant concentration in China (over 521,000), followed by the United States and other countries. Attackers exploiting these vulnerabilities could gain control over vulnerable servers simply by having anonymous read access, such as through public mirrors. This access could lead to the extraction of sensitive data like SSH keys or even allow attackers to overwrite critical files on connected clients.
In light of these vulnerabilities, it is crucial for organizations using Rsync to take immediate action:
- Upgrade to Version 3.4.0: All users are strongly advised to upgrade their Rsync installations to version 3.4.0 or later, which addresses all identified vulnerabilities.
- Configuration Review: For those unable to upgrade immediately, it is recommended to configure the Rsync daemon to require authentication instead of allowing anonymous access.
- Network Security Measures: Organizations should consider blocking TCP port 873, commonly used by Rsync, at the perimeter firewall until they can secure their installations.
- Regular Security Audits: Conduct routine assessments of your systems and configurations to identify potential vulnerabilities and ensure compliance with best practices.
The exposure of over 660,000 Rsync servers to critical vulnerabilities highlights a significant risk in cybersecurity infrastructure. As cyber threats continue to evolve, maintaining up-to-date software and implementing robust security measures are essential for protecting sensitive data and preventing unauthorized access. The recent disclosures serve as a reminder of the importance of vigilance in cybersecurity practices and the need for organizations to act swiftly in response to emerging threats.
2024 US Healthcare Data Breaches: 585 Incidents, 180 Million Compromised User Records
In a troubling trend for the healthcare sector, 2024 witnessed 585 data breaches that compromised the personal information of approximately 180 million individuals. This alarming statistic highlights the escalating threat posed by cyberattacks targeting healthcare organizations, which are increasingly becoming prime targets for malicious actors.
According to the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services (HHS), the vast majority of these incidents were attributed to hacking or IT-related issues, accounting for 421 of the reported breaches. The top two incidents alone had catastrophic impacts: Change Healthcare experienced a breach affecting 100 million individuals, while Kaiser Foundation Health Plan reported a breach impacting 13.4 million individuals. These incidents underscore the vulnerabilities inherent in healthcare systems that often rely on outdated technologies and inadequate security measures.
The types of attacks observed in 2024 included ransomware, unauthorized access, and data leaks. Attackers frequently exploited vulnerabilities in network servers and third-party applications to gain access to sensitive data. For instance, many breaches involved phishing attacks that tricked employees into providing access credentials or downloading malware that compromised systems. The HIPAA (Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act) regulations require healthcare organizations to implement stringent security measures to protect electronic protected health information (ePHI). However, the rapid increase in cyberattacks suggests that many organizations are not adequately prepared to defend against these threats. The database cataloguing all these attacks can be viewed here.
In response to the rising number of breaches, HHS and the Office for Civil Rights have proposed updates to HIPAA Security Standards aimed at enhancing protections for ePHI. Proposed measures include mandatory encryption of sensitive data, implementation of multi-factor authentication, and comprehensive inventory management of technology assets. These changes are intended to fortify defenses against future attacks and ensure compliance with evolving cybersecurity standards.
The data breaches reported in 2024 serve as a stark reminder of the vulnerabilities within the U.S. healthcare system. With millions of records compromised, it is crucial for healthcare organizations to prioritize cybersecurity measures and adopt best practices to safeguard patient information. As cyber threats continue to evolve, proactive measures will be essential in protecting sensitive data from exploitation and ensuring patient trust in healthcare systems.
Cisco’s New AI Application Security Solution
Cisco has recently unveiled its new AI Defense solution, designed to enhance the security of artificial intelligence (AI) applications within enterprises. As organizations increasingly adopt AI technologies, they face unique security challenges that traditional measures often fail to address. Cisco’s AI Defense aims to provide comprehensive protection throughout the lifecycle of AI applications, from development to deployment.
The AI Defense solution focuses on two critical areas: securing the development and deployment of AI applications and safeguarding access to these applications. Key features include:
- AI Application Discovery: This feature allows organizations to identify both sanctioned and shadow AI applications operating within their environments. By gaining visibility into all AI tools in use, security teams can better manage risks associated with unauthorized applications.
- Model Validation: Continuous validation of AI models is crucial for ensuring their reliability and security. Cisco’s solution incorporates automated testing processes that assess models for vulnerabilities, unexpected behaviors, and potential safety issues. This proactive approach helps prevent harmful outcomes before they can impact users.
- Runtime Security: Cisco AI Defense provides ongoing protection against various threats, including prompt injection attacks and data leakage. By monitoring model behavior in real-time, the solution can quickly detect anomalies and respond to potential security incidents.
The launch of AI Defense comes in response to the growing complexity of cybersecurity threats associated with AI technologies. As organizations incorporate proprietary data into their models, the risk of data breaches and exploitation increases significantly. Cisco emphasizes that businesses cannot afford to sacrifice safety for speed when adopting AI solutions. Jeetu Patel, Cisco’s Executive Vice President and Chief Product Officer, highlighted the importance of a robust security framework that allows organizations to innovate confidently while maintaining strong defenses against evolving threats.
Set to be available in March 2025, Cisco’s AI Defense represents a significant advancement in securing AI applications across diverse environments. By integrating advanced machine learning capabilities and leveraging insights from Cisco’s Security Cloud, this solution aims to empower organizations to embrace AI technologies while ensuring comprehensive protection against vulnerabilities and cyber threats. For more information on Cisco AI Defense, visit the official Cisco website.
This wraps up today’s issue. Wherever you are out there in the digital world just stay safe, install the latest patches and keep a watchful eye out for anything that might want to deceive you. Thank you so much for being a wanderer on The Cybersecurity Express and we look forward to welcoming you on board the next time.